Source: pixabay.com
With the growing popularity of cannabis products, users are getting more curious about CBD and THC.
These two main cannabinoids of the Cannabis Sativa plant, first identified in the 1940s, are now becoming household names. Even some of the most famous celebrities and athletes endorse CBD and THC.
While these cannabinoids share similarities, they also have key differences. Today we will discuss those differences to help you decide which cannabinoid best suits your needs.
Chemical Structures
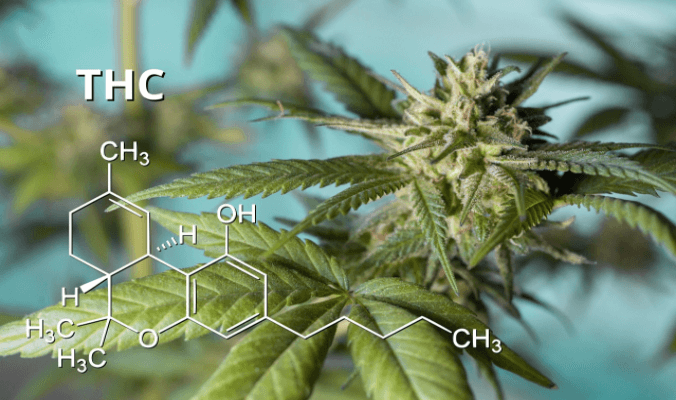
For the most part, THC and CBD have similar chemical structures with 21 carbon, 30 hydrogen, and 2 oxygen atoms. What makes them different is how these atoms are arranged. An extra carbon-oxygen bond in THC makes this cannabinoid an isomer of CBD.
While this difference might seem insignificant, it affects how these compounds react with your body. Due to their similarities with your body’s natural endocannabinoids, THC and CBD interact with your cannabinoid receptors, CB1 and CB2.
However, due to their slight structural difference, THC binds differently than CBD to these receptors and invokes more intense responses.
Psychoactive Effects
Both CBD and THC can help you combat stress in your busy life. However, one cannabinoid has more psychoactive effects than the other. That cannabinoid is THC.
THC attaches to CB1 receptors in your brain to create a euphoric high. Meanwhile, CBD only interacts with the cannabinoid receptors without binding to them. Some claim that CBD is a non-psychoactive cannabinoid, but that is not true. CBD is psychoactive as well. However, it’s not as intoxicating as THC.
When these cannabinoids are consumed together, CBD can keep some THC molecules from binding to endocannabinoid receptors and mitigate their unpleasant psychoactive effects.
Ingestion Methods
Like other cannabis-derived goods such as Delta-8, HHC, and THC-P products, THC and CBD come in various forms, including:
- Blunts and joints: Inhaling cannabis smoke delivers THC, CBD, and other cannabinoids into the lungs, providing quick onset but relatively short duration of effects.
- Vapes: Vaporizers heat cannabis flower or extract to a specific temperature, allowing users to inhale the cannabinoids without combustion or smoke.
- Edibles: When ingested, edibles such as gummies, cookies, or capsules are metabolized by the liver, resulting in delayed onset but potentially longer-lasting effects.
- Oils and tinctures: These products are placed under the tongue for quick absorption into the bloodstream. Sublingual administration allows for relatively rapid onset compared to edibles.
CBD and THC are both available in these forms. However, joints and edibles are the most common methods for using THC-based products.
Medicinal Properties
Source: pixabay.com
Just as nature-made products like black seed oils, CBD and THC are natural supplements with immense therapeutic potential.
People use CBD and THC to manage symptoms of various ailments. Epilepsy is one of the more notable medical conditions that can be treated with CBD. FDA has even approved a CBD-based medication called Epidiolex for rare forms of epilepsy.
There are also FDA-approved THC-based medications such as Nabilone and Dronabinol targeting chemotherapy-induced nausea and appetite loss. These two cannabinoids are also showing potential in managing
- Pain
- Glaucoma
- Inflammation
- Sleep disorders
- PTSD
- Anxiety
- And more
THC and CBD can be used for similar conditions. However, THC might work better for some disorders, while patients with other disorders might prefer the less-psychoactive effects of CBD.
Side Effects
CBD, even in high doses, is a well-tolerated and safe substance. Any side effects accompanying CBD usage might be caused by drug interactions and impurities in the products.
Common side effects of CBD that some users might experience include:
- Diarrhea
- Dizziness
- Dry mouth
- Drowsiness
- Appetite changes
Unlike CBD, high doses of THC will cause side effects. Although temporary, these adverse effects can be intense and include:
- Paranoia
- Red eyes
- Dry mouth
- Increased heart rate
- Impaired coordination
- Impaired cognitive function
- Increased appetite (the munchies)
Source and Legality
The primary source of CBD is hemp, while THC mostly comes from cannabis. The legal status of the two cannabinoids also differs.
CBD’s legality varies depending on the source and its THC content. According to the 2018 Farm Bill, CBD products are legal if they contain no more than 0.3% THC.
However, THC is still classified as a controlled substance in many jurisdictions. Some states allow the recreational use of high-THC products. Others permit its use with a state-issued medical marijuana card for qualified patients with certain health conditions.
Since the laws surrounding marijuana and cannabis-derived products are constantly changing, you should always check your state’s latest regulations before purchasing anything CBD or THC-based.
Drug Testing
Standard drug tests look for THC in the body. While CBD-sensitive tests are also available, they are not used as much.
However, it’s crucial to note that some CBD products may contain traces of THC. For instance, full-spectrum CBD oils with up to 0.3% THC or products with impurities and false claims may cause you to test positive for THC.
People subject to regular drug testing in their workplace should opt for CBD isolates or broad-spectrum products with zero THC to stay safe.
Make An Informed Purchase
By knowing the differences between CBD and THC, you can make your next cannabis purchase an informed one. These cannabinoids have the potential to soothe discomfort naturally and help you live a better life. So, embrace them now and start your cannabis journey!